Unveiling the Manufacturing Secrets Behind Sugar Cane and Its Diverse Array of Products
The manufacturing trip of sugar cane is elaborate and multi-faceted. It starts in the areas, where mindful harvesting methods established the phase for ideal sugar extraction. The process entails several stages, including juice extraction and refining - sugar cane products. However, sugar cane's potential prolongs much past plain sweetness. Developments in handling and lasting methods are improving its function in modern sectors. What exists ahead for this flexible crop? The answers may stun those thinking about its future
The Journey of Sugar Cane: From Area to Factory

As sugar cane guides carefully in the exotic wind, it starts a transformative journey from area to manufacturing facility. The vibrant eco-friendly stalks, rich in sucrose, are cultivated under suitable problems, benefiting from adequate sunlight and rainfall. Farmers carefully keep track of the growth, making certain the plants reach their peak maturation, which is vital for making best use of sugar content.Once matured, the cane is prepared for harvesting, where its coarse framework holds the pledge of wonderful products. The trip proceeds as the stalks are transported to refining centers, where they undergo a series of thorough steps. At the manufacturing facility, the cane is washed, shredded, and pressed to draw out the juice. This juice is then cleared up and vaporized, leading the means for formation. Each phase of this trip is vital, as it eventually establishes the high quality of the sugar and other products stemmed from this versatile plant.
Harvesting Methods: The Initial Step in Production
Gathering sugar cane requires accuracy and skill, as the timing and strategy directly influence the top quality of the final item. The process typically begins with establishing the perfect harvest time, which is essential; sugar material peaks right before the plant gets to complete maturity. Cultivators commonly rely upon experience and agricultural signs to decide when to harvest.Two main strategies dominate the gathering landscape: handbook and mechanical approaches. Hands-on harvesting, though labor-intensive, permits careful selection of stalks and decreases damage. Employees use machetes to reduce the cane near to the base, guaranteeing the stalks remain undamaged for processing.Mechanical harvesting, on the other hand, utilizes customized equipment to reduce and collect the cane promptly. While this technique considerably raises effectiveness, it might result in higher degrees of debris and lower sugar content. Ultimately, the selected technique influences not only the quantity however additionally the high quality of sugar cane delivered to refining centers.
The Removal Refine: Opening the Sweetness
The extraction process is crucial for changing gathered sugar cane right into wonderful juice. Various techniques of juice removal can significantly affect the high quality and return of the end product. Recognizing these strategies is vital for taking full advantage of the advantages of sugar cane manufacturing.
Harvesting Methods Clarified
Releasing the sweet taste of sugar cane begins with precise harvesting techniques that ensure optimal return and top quality. The process commonly includes cutting the cane at ground level, making sure marginal damages to the plant and permitting regrowth. Harvesters often utilize machetes or specialized machines, depending upon the range of the operation. Timing is crucial; gathering takes place when the sugar material reaches its optimal, normally during dry seasons. In addition, employees must be educated to identify the best stalks, staying clear of those that are also old or infected. Effective transportation to refining centers is likewise important, as hold-ups can result in sugar deterioration (sugar cane products). These meticulous methods ultimately lay the foundation for creating high-grade sugar and its diverse byproducts
Juice Removal Approaches
Juice extraction is a crucial action in transforming sugar cane into its sweet significance. This procedure commonly entails numerous approaches, each created to efficiently remove the sugary fluid from the fibrous stalks. One of the most usual technique is milling, where the sugar cane is smashed in between hefty rollers to release the juice. An additional approach is diffusion, which utilizes hot water to liquify the sugar from the cane fibers, making it a much more effective option for large procedures. Furthermore, some producers utilize screw presses, which apply mechanical pressure to essence juice. After extraction, the juice undergoes information to remove impurities before additional handling. Each method mirrors the industry's emphasis on maximizing yield and making sure top notch sugar production.
Refining Sugar: Transforming Raw Cane Into Granulated Gold
The refining procedure is vital for converting raw cane sugar into the pure, granulated item customers recognize. sugar cane products. This includes a collection of removal and filtering actions to eliminate impurities, complied with by formation and drying out strategies that boost the sugar's top quality. Recognizing these techniques reveals the complex makeover from cane to the gold granules that sweeten numerous foods and beverages
Removal and Filtering Refine
A crucial stage in the sugar manufacturing journey entails the extraction and purification of juice from newly gathered sugar cane. This procedure starts with squashing the cane to release its sweet juice, generally using huge rollers or mills. The drawn out juice contains not just sugar but additionally contaminations, consisting of fibers and mud. To ensure the juice appropriates for more refining, it undertakes a purification procedure. This involves passing the juice through numerous filters and clarifiers to remove strong particles and undesirable products. Chemicals such as lime may be included in assist in the explanation procedure. The outcome is a clear, raw cane juice that works as the foundation for generating refined sugar, all set for succeeding phases of handling.

Condensation and Drying Techniques
After the extraction and purification processes yield clear raw cane juice, the these details next action in sugar manufacturing is crystallization. This procedure includes boiling the juice to evaporate water, enabling sugar particles to form crystals. check As the fluid thickens, it reaches supersaturation, prompting sugar to crystallize. The mixture is then cooled, promoting additional crystal development. Once crystallization is full, the sugar crystals are separated from the remaining syrup through centrifugation.The last involves drying out, where the crystals are revealed to warm air to eliminate recurring wetness. This action is necessary, as it assures the item achieves the preferred granulation and rack security. The result is pure, granulated sugar, ready for product packaging and distribution.
Beyond Sweetness: Diverse Products From Sugar Cane
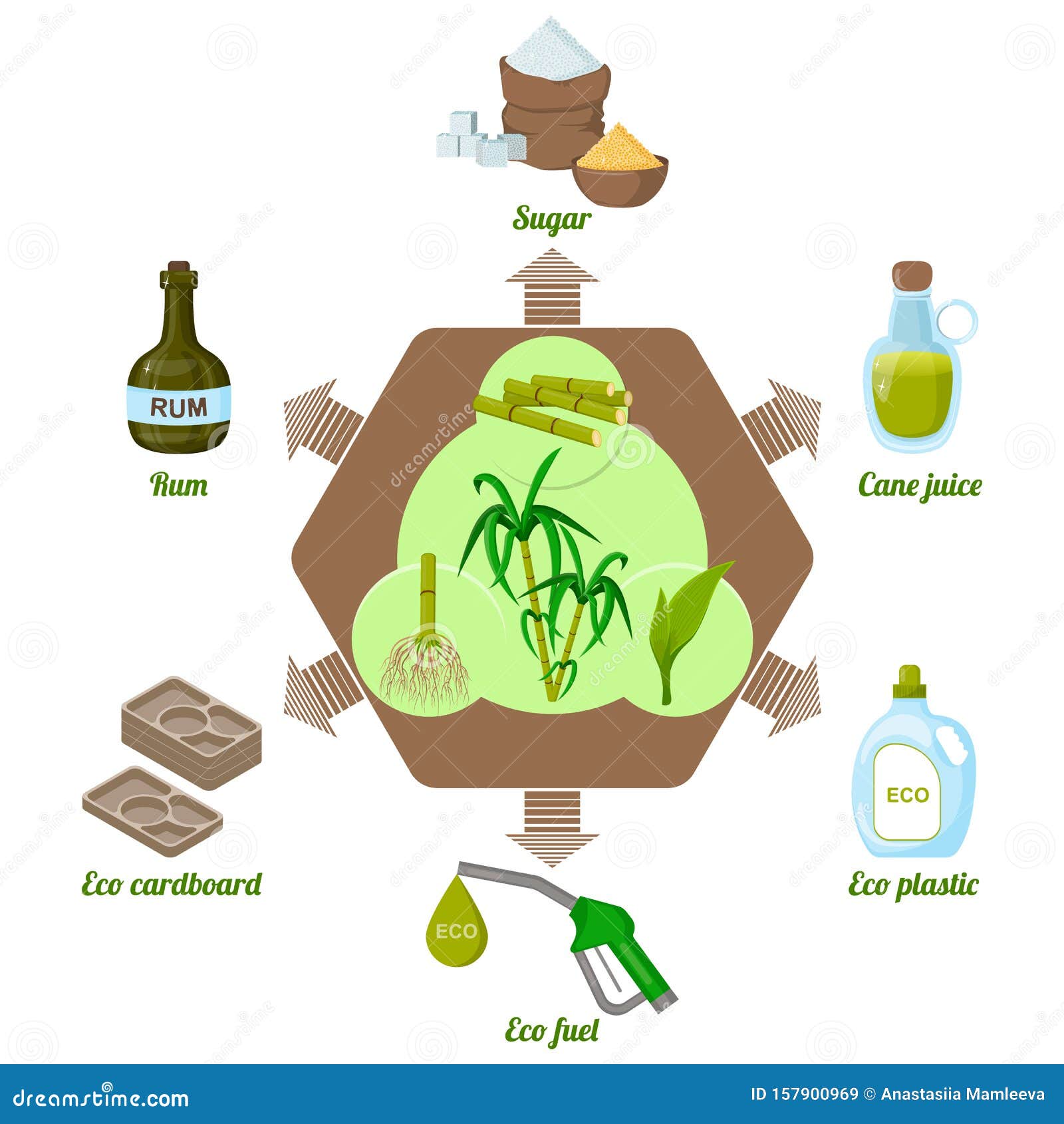
While sugar cane is primarily acknowledged for its wonderful flavor, its convenience prolongs far past simple sweetness. This resilient plant works as the resource for a myriad of products that satisfy diverse markets. Ethanol, originated from sugar cane fermentation, plays an important role in renewable resource, functioning as a cleaner option to nonrenewable fuel sources. Furthermore, molasses, a byproduct of sugar refining, is made use of in pet feed, in addition to in baking and fermentation processes.Sugar cane's coarse residue, referred to as bagasse, is not wasted; it is transformed right into naturally degradable packaging materials and acts as a biomass gas source. Moreover, different sugars and syrups obtained from sugar cane find applications in the food and beverage market, adding to flavoring and conservation. The plant's fallen leaves can be used for thatching, while its juice is consumed as a rejuvenating drink in many societies. Subsequently, sugar cane exhibits agricultural possibility past its sugary track record.
Advancements in Sugar Cane Handling
As advancements in modern technology remain to reshape various sectors, sugar cane handling is experiencing a substantial makeover. Modern advancements, consisting of automated harvesting and precision farming, are boosting effectiveness and return. Drones and sensing units monitor crop health and wellness, allowing farmers to optimize irrigation and nutrient application, ultimately enhancing productivity.In handling facilities, advanced machinery and equipment streamline operations. Innovations such as chemical handling and advanced purification strategies enhance the extraction of sugar while lessening waste. In enhancement, the fostering of real-time data analytics makes it possible for producers to monitor processes carefully, making certain quality assurance and minimizing downtime.Biotechnology is likewise playing a crucial role; genetic modifications boost sugar cane's resistance to parasites and ecological stress factors. These advancements not only add to higher sugar yields yet also help with see this the manufacturing of diverse by-products from the cane, expanding its industrial applications. In general, these innovations are leading the way for an extra effective and sustainable sugar cane processing market.
The Future of Sugar Cane: Sustainability and Bioproducts
The future of sugar cane manufacturing is progressively linked with sustainability and the advancement of bioproducts. As worldwide demand for eco-friendly options rises, the sugar cane industry is pivoting towards practices that minimize environmental impact. Advancements in cultivation strategies, such as accuracy agriculture and incorporated insect monitoring, objective to enhance yield while minimizing resource consumption.Furthermore, sugar cane is being discovered as a basic material for biofuels, bioplastics, and other lasting products. These bioproducts not only use a sustainable alternative to standard nonrenewable fuel sources and plastics yet likewise add to a round economic climate by utilizing waste materials.Research and growth in biotechnology are leading the method for enhanced sugar cane ranges that require much less water and fertilizers, further promoting sustainability. By embracing these developments, the sugar cane sector can secure its future while addressing crucial environmental challenges, demonstrating its potential as a keystone of sustainable development.
Often Asked Concerns
What Are the Ecological Impacts of Sugar Cane Farming?
The environmental effects of sugar cane farming include deforestation, soil degradation, and water air pollution. Additionally, making use of chemicals can hurt biodiversity, while monoculture methods reduce environment resilience, posturing lasting sustainability difficulties for farming practices.
How Does Sugar Cane Contrast to Various Other Sweeteners Nutritionally?
Sugar cane, rich in carbohydrates, offers power however lacks vital nutrients compared to options like honey or maple syrup, which use minerals and vitamins. Its high glycemic index likewise raises worries over blood glucose spikes.
What Are the Health And Wellness Conveniences of Consuming Sugar Cane Products?
The health benefits of consuming sugar cane items consist of boosted food digestion, enhanced power levels, and possible antioxidant residential or commercial properties. In addition, they may sustain hydration and offer essential vitamins and minerals, contributing positively to general well-being.
How Is Sugar Cane Waste Utilized After Processing?
After handling, sugar cane waste is utilized in various methods, including biofuel manufacturing, pet feed, and organic fertilizers. This sustainable technique lowers environmental influence while optimizing source efficiency within the sugar market.
What Are the Historical Origins of Sugar Cane Cultivation?
